Last updated on September 9th, 2025 at 10:55 pm
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
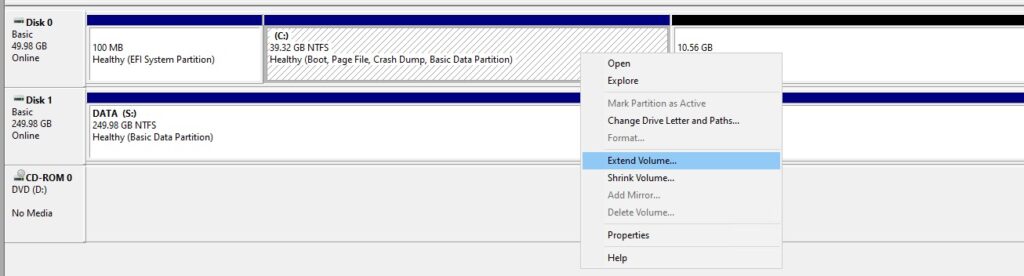
When trying to extend virtual hard drive, you might encounter an issue where the recovery partition is situated between the main partition and the unallocated space. Below is an example of this happening:
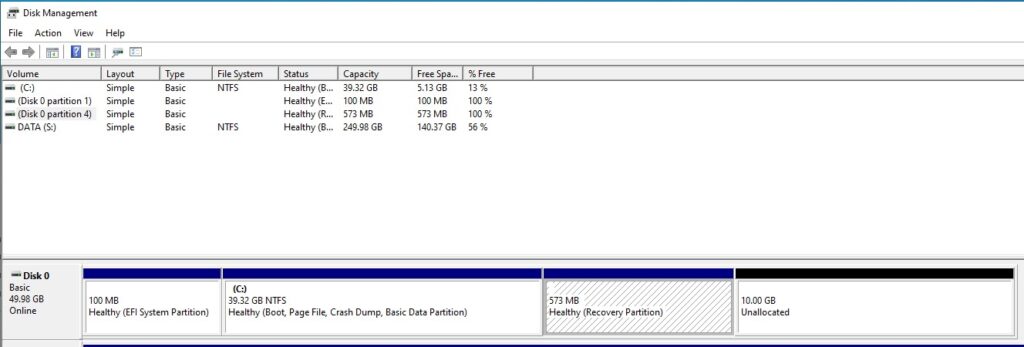
This guide walks you through the process of safely removing the recovery partition, extending the main partition, and optionally recreating the recovery partition afterward.
Warning
Deleting the recovery partition removes your system’s recovery tools. Proceed at your own risk, and ensure you have a full system backup before starting.
Steps to Delete the Recovery Partition
To extend your virtual hard drive, you need to delete the recovery partition first. Here’s how:
1. Open Command Prompt as Administrator
- Search for Command Prompt in your Start menu.
- Right-click and select Run as administrator.
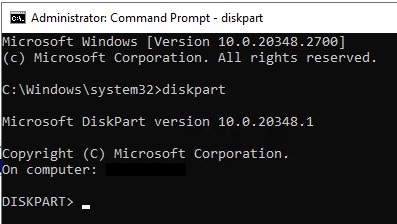
2. Use DiskPart to Delete the Recovery Partition
DiskPart is a command-line utility for managing disk partitions. Follow these steps:
- Enter DiskPart:
diskpart - List available disks:
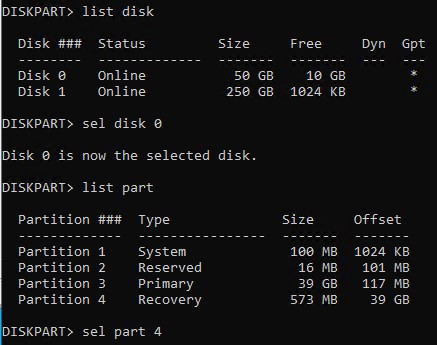
list diskIdentify the disk containing the recovery partition (e.g., Disk 0). - Select the disk:
select disk 0(Replace 0 with the appropriate disk number.) - List the partitions on the selected disk:
list partitionIdentify the recovery partition by size or position. - Select the recovery partition:
select partition X(Replace X with the partition number for the recovery partition.)
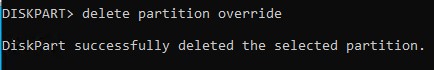
- Delete the recovery partition:
delete partition override
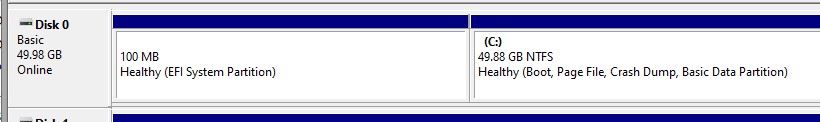
3. Extend the Primary Partition
With the recovery partition deleted, you can now extend your main partition using Disk Management or DiskPart.
Using Disk Management:
- Right-click on the main partition in Disk Management.
- Select Extend Volume and follow the prompts.
Using DiskPart:
select partition Y
extend(Replace Y with the main partition number.)
Optional: Recreate the Recovery Partition
If you want to restore the recovery partition after resizing your primary partition, follow these steps:
1. Add Space for the Recovery Partition
Allocate a small amount of unallocated space (e.g., 500 MB) at the end of the extended disk. Ensure your disk uses the GPT partition style.
2. Create a New Recovery Partition
- Open DiskPart and select the disk:
select disk 0(Replace 0 with the appropriate disk number.) - Create a recovery partition:
select partition Z create partition primary id=de94bba4-06d1-4d40-a16a-bfd50179d6ac gpt attributes=0x8000000000000001(Replace Z with the unallocated space partition number.)
3. Enable Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)
Once the recovery partition is created, re-enable WinRE:
- Set the recovery image path:
REAGENTC.EXE /setreimage /path <dir_name> [/target <dir_name>] [/logpath <file_path>]Example:REAGENTC.EXE /setreimage /path r:\Recovery\WindowsRE /logpath C:\Temp\Reagent.log REAGENTC.EXE /setreimage /path r:\Recovery\WindowsRE /target C:\Windows - Enable WinRE:
reagentc /enable
Example Commands Recap
Delete the Recovery Partition:
delete partition overrideRecreate the Recovery Partition:
create partition primary id=de94bba4-06d1-4d40-a16a-bfd50179d6ac
gpt attributes=0x8000000000000001Enable WinRE:
REAGENTC.EXE /setreimage /path r:\Recovery\WindowsRE /logpath C:\Temp\Reagent.log
REAGENTC.EXE /setreimage /path r:\Recovery\WindowsRE /target C:\Windows
reagentc /enable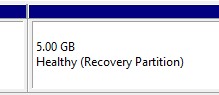
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the recovery partition, and why is it important?
The recovery partition contains tools and files to repair your Windows installation or reset the system to factory settings. Removing it disables these features unless recreated.
Will deleting the recovery partition affect my data?
No, deleting the recovery partition will not impact your personal files or primary partitions. However, it removes recovery tools, so create a backup or recovery disk before proceeding.
What does the delete partition override command do?
This command forces the deletion of a partition, bypassing restrictions that normally protect system or recovery partitions.
How much space should I allocate for the recovery partition?
Allocate at least 500 MB of space for the recovery partition.
Can I undo the deletion of the recovery partition?
Not directly. You must recreate it and reconfigure WinRE as described above.
Glossary
- DiskPart: A command-line disk partitioning utility in Windows.
- Recovery Partition: A dedicated partition containing tools for repairing or resetting Windows.
- WinRE: Windows Recovery Environment, used for troubleshooting and recovery.
- GPT (GUID Partition Table): A partitioning scheme that supports larger disks and more partitions than MBR.
- Unallocated Space: Free disk space not assigned to any partition.
Discover more from TechyGeeksHome
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
