Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
VMware vSphere HA (High Availability) is a feature that provides automated failover capabilities for virtual machines running on VMware vSphere hosts. When a host failure occurs, HA will detect it and restart the affected virtual machines on another available host in the cluster.
If you are experiencing a failover error with VMware vSphere HA, there are several possible causes. Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot the issue:
- Check the vSphere HA cluster configuration: Make sure that the vSphere HA cluster is properly configured and that all hosts are members of the same cluster. Also, check that the vSphere HA admission control policy is configured correctly.
- Check the network configuration: Ensure that the network configuration is correct and that all hosts can communicate with each other. Verify that the network redundancy is set up correctly and that there are no network issues such as high latency or packet loss.
- Check the vSphere HA agent: Make sure that the vSphere HA agent is running on all hosts in the cluster. Check the status of the vSphere HA agent and restart it if necessary.
- Check the vSphere HA master node: Verify that the vSphere HA master node is functioning correctly. If the master node is not working properly, it may not be able to perform a failover.
- Check the virtual machine settings: Ensure that the virtual machine settings are configured correctly for vSphere HA. Verify that the virtual machine has been added to the HA cluster and that the admission control policy is not blocking the virtual machine.
Disable and Enable vSphere HA
To disable and enable the vSphere HA in the vSphere Web Client, follow these simple steps:
Log in to the vSphere Web Client. The default URL is:
https://vCenter_Server_FQDN:9443/vsphere-client
Disable vSphere HA
- In the Home screen, click Hosts and Clusters.
- Locate the cluster.
- Right-click the cluster and click Settings.
- Click vSphere HA located under Services.
- Click Edit.
- Deselect the Turn On vSphere HA option.
Enable vSphere HA
- To enable vSphere HA, repeat the above steps and select Turn on VMware HA option.
- Click OK.
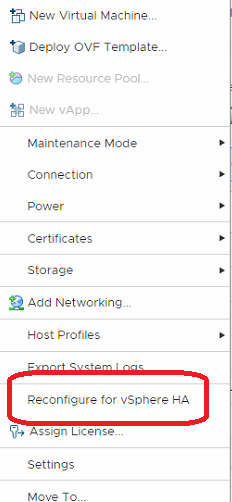
Reconfigure vSphere HA
If the above guides still do not work, then you can try right-clicking on a host and selecting Reconfigure for vSphere HA:
If none of these steps resolve the issue, you may need to contact VMware support for further assistance.
FAQ
What is vSphere HA in VMware?
vSphere HA (High Availability) is a feature in VMware vSphere that provides automatic restart of virtual machines (VMs) when a physical host fails. This feature monitors the health of the hosts in a cluster and automatically restarts any virtual machines that were running on a failed host on another available host within the cluster.
What is the difference between VMware HA and vMotion?
vSphere HA (High Availability) is designed to provide automatic restart of virtual machines (VMs) in the event of a host failure. When a host fails, vSphere HA detects the failure and automatically restarts the affected VMs on other available hosts in the cluster. The goal of vSphere HA is to minimize downtime and ensure that critical applications and services remain available.u003cbru003eu003cbru003evMotion, on the other hand, is a feature that allows live migration of running VMs from one host to another without interruption to the VMs. This migration can be done for a variety of reasons, such as load balancing, hardware maintenance, or upgrading the host software. vMotion uses a shared storage system to move the VM’s files from one host to another, and the VM’s memory state is transferred over a high-speed network. The migration process is transparent to the user, and the VM continues to run as if nothing had happened.
What is the difference between VMware HA and VMware ft?
The main difference between VMware HA and VMware FT is the level of downtime that occurs in the event of a host failure. With VMware HA, there is a brief interruption in service while the VMs are restarted on another host. u003cbru003eu003cbru003eWith VMware FT, there is no interruption of service, as the shadow instance takes over immediately. However, VMware FT requires more resources than VMware HA, as it runs a complete duplicate of the VM on a different host.
What does HA do in vCenter?
HA stands for High Availability, which is a feature of VMware vSphere and vCenter that helps ensure that virtual machines (VMs) are continuously available in the event of a host server failure.u003cbru003eu003cbru003eWhen HA is enabled in vCenter, it creates a cluster of ESXi hosts and monitors the availability of the VMs running on each host. If one of the hosts fails, the VMs that were running on that host are automatically restarted on one of the remaining hosts in the cluster. This ensures that the VMs are quickly recovered and continue to run without disruption.u003cbru003eu003cbru003eHA also provides admission control, which ensures that enough resources are available in the cluster to support the VMs in the event of a host failure. If there are not enough resources available, HA will prevent new VMs from being powered on, to avoid over-committing resources that might be needed in a failover scenario.
Share this content:
Discover more from TechyGeeksHome
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
